Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMDRKH2)
| Drug Name |
Thiamphenicol
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
thiamphenicol; 15318-45-3; Thiophenicol; Thiamcol; (+)-Thiamphenicol; Raceophenidol; Dextrosulphenidol; Thiamphenicolum; D-Thiocymetin; D-Thiophenicol; Thiocymetin (TN); Armai (TN); Thiocymetin; Tiamfenicolo [DCIT]; UNII-FLQ7571NPM; Tiamfenicol [INN-Spanish]; Thiamphenicol (Thiophenicol); Macphenicol; C12H15Cl2NO5S; Urfamycine; Igralin; Hyrazin; Dexawin; Rincrol; Neomyson; Urfamicina; Thiamphenicolum [INN-Latin]; Descocin; Masatirin; Efnicol; SW 5063; Unaseran-D; Thiamphenicol [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; EINECS 239-355-3; RACEPHENICOL; WIN-5063-2
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
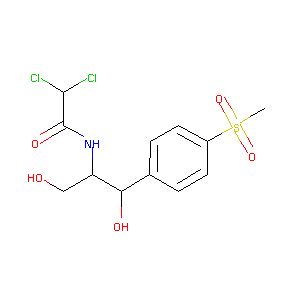 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 356.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
